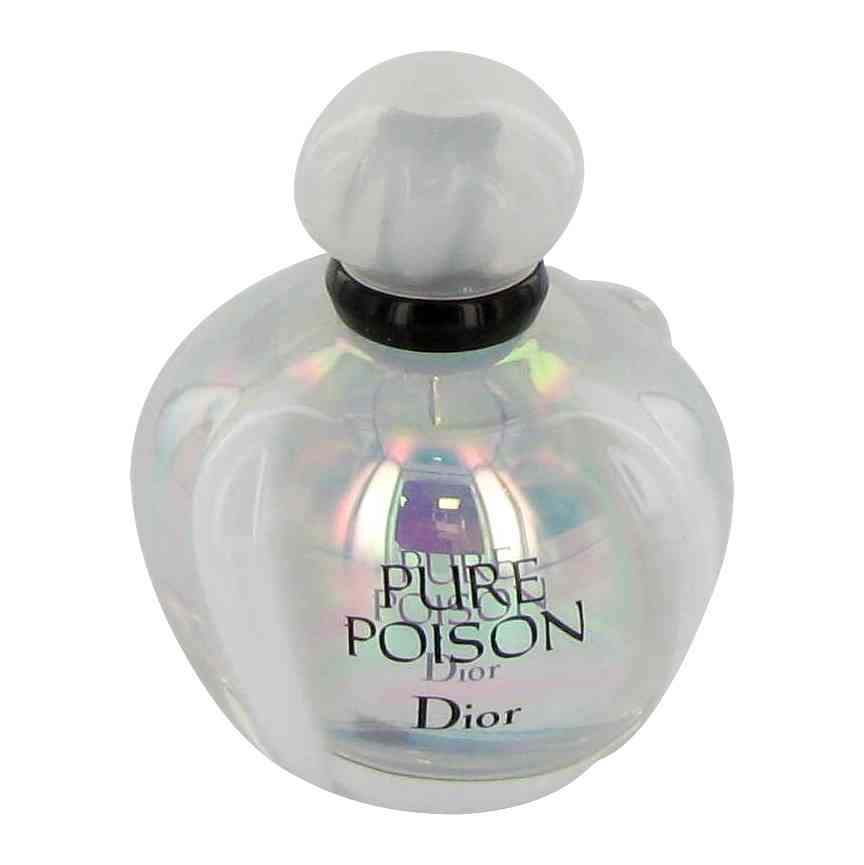
Pure Poison Perfume
Women's Fragrance
Pure Poison perfume: A Christian Dior fragrance launched in 2004. A perfume for women that suggest passion. A ladies perfume for any occasion.
Aroma Notes: Jasmine, Gardenia, Sandalwood, Musk, Amber and Orange.
Jasmine
Jasmine is considered an absolute and not an essential oil as the petals of the flower are much too delicate and would be destroyed by the distillation process used in creating essential oils. Other than the processing method it is essentially the same as an essential oil. Absolute is a technical term used to denote the process of extraction. It is in common use. Its flowers are either extracted by the labor-intensive method of enfleurage or through chemical extraction. It is expensive due to the large number of flowers needed to produce a small amount of oil. The flowers have to be gathered at night because the odor of jasmine is more powerful after dark. The flowers are laid out on cotton cloths soaked in olive oil for several days and then extracted leaving the true jasmine essence to be used in Pure Poison perfume for women. Some of the countries producing jasmine essential oil are India, Egypt, China and Morocco. Jasmine scent has been reported to have sedative properties. Many species also yield an absolute, which is used in perfumes and incense.
Gardenia
Gardenia taitensis (also called Tahitian Gardenia or Tiaré Flower) is a species of plant in the Rubiaceae family. It is an evergreen tropical shrub that grows to 4 m tall, it has glossy dark green leaves (5–16 cm long) that are oppositely arranged along the stem. The flower is creamy white, pinwheel-shaped with 5 to 9 lobes (each lobe 2–4 cm long) and very fragrant. Native to the highland shores of the South Pacific, it has the distinction of being one of the few cultivated plants native to Polynesia.
It is the national flower of French Polynesia and the Cook Islands.The name Tahitian Gardenia is somewhat a misnomer because it is neither native nor naturalized in Tahiti. The first acceptable scientific name for the plant was based on Tahitian specimens collected by Jules Dumont d'Urville in 1824. Hence the scientific name of Gardenia taitensis, and the English name of Tahitian Gardenia or Tiaré Flower.
It was first collected in Tahiti, by the Forsters on Captain Cook's first Pacific voyage (1768–1771), although it was misidentified as Gardenia Florida. The plant originates from Melanesia and Western Polynesia. It is an aboriginal introduction to the Cook Islands and French Polynesia and possibly Hawaii. Polynesian people in the pacific islands use the extremely fragrant blooms in their flower necklaces, which are called "Ei" in the Cook Islands, "Hei" in Tahiti or "Lei" in Hawaii".
In some Pacific island traditions, wearing a flower indicates relationship status. A flower worn on the left ear means the person is taken and on the right ear means available. The plant is believed to have medicinal properties to treat several ailments. In Tonga a bark infusion is dripped into the nose, eyes and mouth to treat "ghost sickness".
In Samoa parts of the plant are used to treat inflammation. The flower is used to make Monoi Tiare Tahiti, a perfume-oil used in Pure Poison perfume made by infusing the blossoms in coconut oil (see enfleurage).Tiare is also used in niche perfumery but its prohibitively high cost excludes use in commercial perfumery. Notable examples include Tiare by Ormonde Jayne launched in 2009 and Tiare by Chantecaille.
The Tiare flowers are hand picked and then laid unopened in oil for 15 days to obtain the extract.
Sandalwood
Sandalwood oil is an essential oil obtained from the steam distillation of chips and billets cut from the heartwood of the sandalwood tree. Sandalwood oil is used in Pure Poison perfume/perfumery, cosmetics, and sacred unguents. Sandalwood essential oil is used in medicine for the treatment of both somatic and mental disorders. A study investigating the effects of inhalation of East Indian sandalwood oil and its main compound, α-santalol, on human physiological parameters found that the compounds elevated pulse rate, skin conductance, and systolic blood pressure.
Musk
Musk is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in Pure Poison perfume/perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. Musk was a name originally given to a substance with a penetrating odor obtained from a gland of the male musk deer. The substance has been used as a popular perfume fixative since ancient times and is one of the more expensive animal products in the world.
The name originates from the Sanskrit word for "testicle", and has come to encompass a wide variety of aromatic substances with similar odors despite their often differing chemical structures. Until the late 19th century, natural musk was used extensively in perfumery until economic and ethical motives led to the adoption of synthetic musk, which is now used almost exclusively. The organic compound primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of musk is muscone.
Amber and Pure Poison Perfume
Amber is fossilized tree resin (not sap), which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. "Amber" perfumes may be created using combinations of labdanum, benzoin resin, copal (itself a type of tree resin used in incense manufacture), vanilla, Dammara resin and/or synthetic materials.
Labdanum is produced today mainly for the perfume industry. The raw resin is usually extracted by boiling the leaves and twigs. An absolute is also obtained by solvent extraction. An essential oil is produced by steam distillation.
The raw gum is a black (sometimes dark brown), fragrant mass containing up to 20% or more of water. It is plastic but not pourable, and becomes brittle with age. The absolute is dark amber-green and very thick at room temperature. The fragrance is more refined than the raw resin.
The odor is very rich, complex and tenacious. Labdanum is much valued in perfumery because of its resemblance to ambergris, which has been banned from use in many countries because its precursor originates from the sperm whale, which is an endangered species: although the best-quality ambergris is found free-floating or washed up onshore (long exposure to sunlight, air and water removes offensive-smelling components of the fresh substance), and thus raises no ethical objections, a lower-quality version can also be recovered from some fraction of freshly slaughtered whales, and so may encourage poaching of sperm whales. Labdanum is the main ingredient used when making the scent of amber in woman perfume/perfumery. Labdanum's odor is variously described as amber, animalic, sweet, woody, ambergris, dry musk, or leathery.
Orange Aroma
Orange oil is an essential oil produced by cells within the rind of an orange fruit. In contrast to most essential oils, it is extracted as a by-product of orange juice production by centrifugation, producing a cold-pressed oil. It is composed of mostly (greater than 90%) d-limonene, and is often used in place of pure d-limonene. D-limonene can be extracted from the oil by distillation.
Limonene gives citrus fruit their familiar aroma, and is therefore used in Pure Poison perfume, a ladies perfume for its fragrance.
Home Page Pure Poison Perfume>Back to Christian Dior the biography Perfume News